转换器和代码生成重构的实现(基础模板编译器部门开始)
现有实现的回顾
现在,让我们从最小示例部门停下的地方开始更认真地实现模板编译器.距离我们上次处理它已经有一段时间了,所以让我们回顾一下当前的实现.主要关键词是 Parse,AST 和 Codegen.
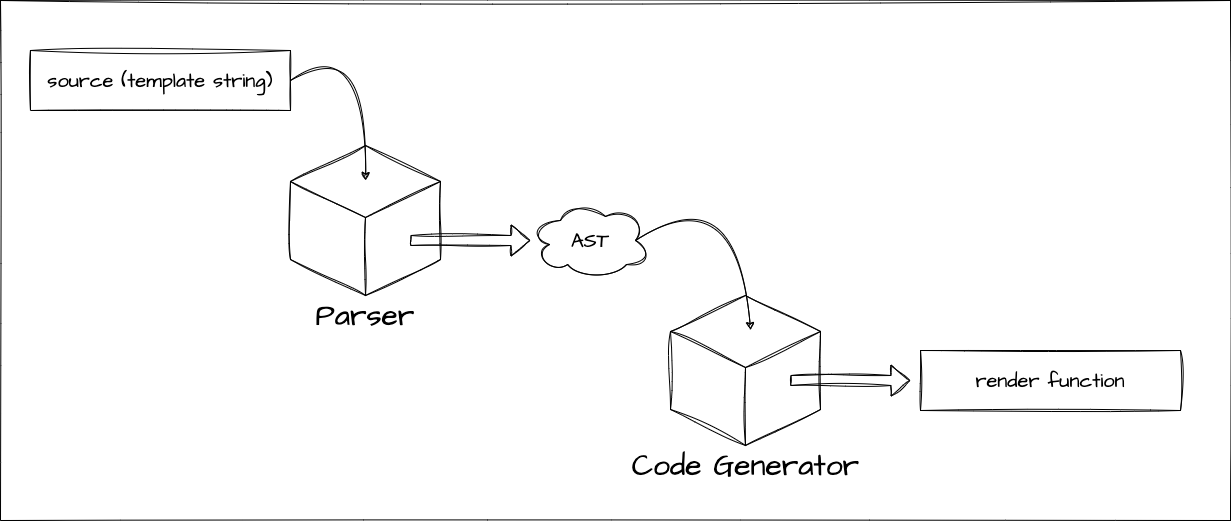
export function baseCompile(
template: string,
option: Required<CompilerOptions>,
) {
const ast = baseParse(template.trim())
const code = generate(ast, option)
return code
}实际上,这个配置与原始配置略有不同.让我们看看原始代码.
你能理解吗...?
export function baseCompile(
template: string,
option: Required<CompilerOptions>,
) {
const ast = baseParse(template.trim())
transform(ast)
const code = generate(ast, option)
return code
}就是这样.
这次,我们将实现 transform 函数.
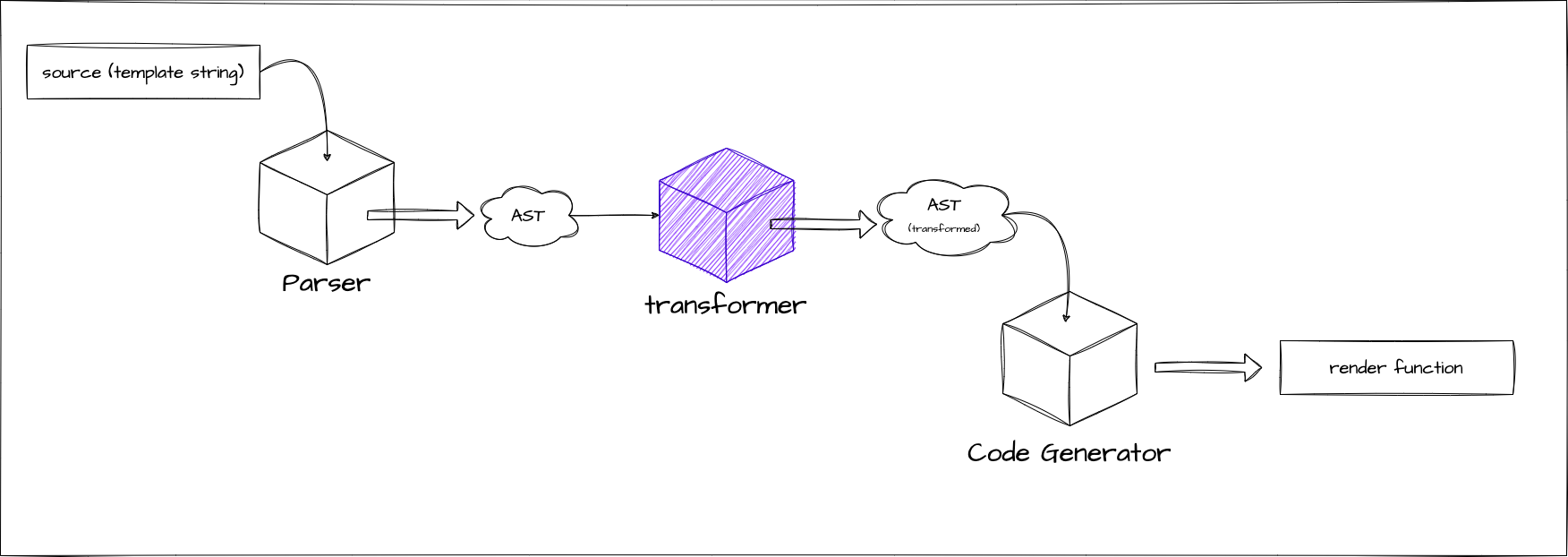
什么是 Transform?
正如你从上面的代码中可以想象的那样,通过解析获得的 AST 被 transform 函数以某种方式转换.
这个 VNODE_CALL 和以 JS 开头的名称的 AST 代码是我们这次要处理的. Vue.js 的模板编译器分为两部分:表示解析模板结果的 AST 和表示生成代码的 AST. 我们当前的实现只处理前一个 AST.
让我们考虑将模板 <p>hello</p> 作为输入的情况.
首先,通过解析生成以下 AST.这与现有实现相同.
interface ElementNode {
tag: string
props: object /** 省略 */
children: (ElementNode | TextNode | InterpolationNode)[]
}
interface TextNode {
content: string
}{
"tag": "p",
"props": {},
"children": [{ "content": "hello" }]
}至于"表示生成代码的 AST",让我们考虑应该生成什么样的代码. 我认为应该是这样的:
h('p', {}, ['hello'])这是表示生成的 JavaScript 代码的 AST. 换句话说,它是一个表示用于生成应该生成的代码的 AST 的对象.
interface VNodeCall {
tag: string
props: PropsExpression
children:
| TemplateChildNode[] // multiple children
| TemplateTextChildNode // single text child
| undefined
}
type PropsExpression = ObjectExpression | CallExpression | ExpressionNode
type TemplateChildNode = ElementNode | InterpolationNode | TextNode{
"tag": "p",
"props": {
"type": "ObjectExpression",
"properties": []
},
"children": { "content": "hello" }
}通过这种方式,表示由 Codegen 生成的代码的 AST 被表达. 你可能在这一点上感觉不到分离它们的必要性,但在将来实现指令时会很有用. 通过分离专注于输入的 AST 和专注于输出的 AST,我们可以使用称为 transform 的函数执行从 input AST -> output AST 的转换.
Codegen 节点
现在我们已经掌握了流程,让我们确认我们将处理什么样的节点(我们想要转换什么样的节点).我将在枚举它们并提供注释的同时进行解释.请参考源代码获取准确信息,因为某些部分被省略了.
export interface SimpleExpressionNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
content: string
isStatic: boolean
identifiers?: string[]
}
// 这表示调用 h 函数的表达式。
// 它假设类似 `h("p", { class: 'message'}, ["hello"])` 的东西。
export interface VNodeCall extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL
tag: string | symbol
props: ObjectExpression | undefined // 注意:在源代码中实现为 PropsExpression(用于未来扩展)
children:
| TemplateChildNode[] // multiple children
| TemplateTextChildNode
| undefined
}
export type JSChildNode =
| VNodeCall
| ObjectExpression
| ArrayExpression
| ExpressionNode
// 这表示一个 JavaScript 对象。它用于 VNodeCall 的 props 等。
export interface ObjectExpression extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.JS_OBJECT_EXPRESSION
properties: Array<Property>
}
export interface Property extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.JS_PROPERTY
key: ExpressionNode
value: JSChildNode
}
// 这表示一个 JavaScript 数组。它用于 VNodeCall 的 children 等。
export interface ArrayExpression extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.JS_ARRAY_EXPRESSION
elements: Array<string | Node>
}转换器设计
在实现转换器之前,让我们谈谈设计.首先,重要的是要注意有两种类型的转换器:NodeTransform 和 DirectiveTransform.这些分别用于转换节点和指令,并采用以下接口.
export type NodeTransform = (
node: RootNode | TemplateChildNode,
context: TransformContext,
) => void | (() => void) | (() => void)[]
// TODO:
// export type DirectiveTransform = (
// dir: DirectiveNode,
// node: ElementNode,
// context: TransformContext,
// ) => DirectiveTransformResult;
export type DirectiveTransform = FunctionDirectiveTransform 将在实现指令时在后面的章节中介绍,所以现在让我们称之为 Function. NodeTransform 和 DirectiveTransform 实际上都是函数.你可以将它们视为转换 AST 的函数. 请注意,NodeTransform 的结果是一个函数.在实现 transform 时,如果你实现它返回一个函数,该函数将在该节点的转换之后执行(它被称为 onExit 过程). 你想在节点的 transform 之后执行的任何处理都应该在这里描述.我将在稍后描述称为 traverseNode 的函数时解释这一点. 接口的解释主要如上所述.
作为更具体的实现,有用于转换元素的 transformElement 和用于转换表达式的 transformExpression 等. 至于 DirectiveTransform 的实现,每个指令都有实现. 这些实现在 compiler-core/src/transforms 中实现.具体的转换过程在这里实现.
图像 ↓
接下来,关于上下文,TransformContext 保存在这些转换期间使用的信息和函数. 将来会添加更多,但现在这就足够了.
export interface TransformContext extends Required<TransformOptions> {
currentNode: RootNode | TemplateChildNode | null
parent: ParentNode | null
childIndex: number
}转换器的实现
现在让我们在实践中看看 transform 函数.首先,让我们从独立于每个转换过程内容的框架的一般解释开始.
结构非常简单,只需生成上下文并使用 traverseNode 函数遍历节点. 这个 traverseNode 函数是转换的主要实现.
export function transform(root: RootNode, options: TransformOptions) {
const context = createTransformContext(root, options)
traverseNode(root, context)
}在 traverseNode 中,基本上,它只是将保存在上下文中的 nodeTransforms(转换节点的函数集合)应用于节点. 对于那些有子节点的,子节点也通过 traverseNode 传递. 在接口解释期间提到的 onExit 的实现也在这里.
export function traverseNode(
node: RootNode | TemplateChildNode,
context: TransformContext,
) {
context.currentNode = node
const { nodeTransforms } = context
const exitFns = [] // 转换后要执行的操作
for (let i = 0; i < nodeTransforms.length; i++) {
const onExit = nodeTransforms[i](node, context)
// 注册转换后要执行的操作
if (onExit) {
if (isArray(onExit)) {
exitFns.push(...onExit)
} else {
exitFns.push(onExit)
}
}
if (!context.currentNode) {
return
} else {
node = context.currentNode
}
}
switch (node.type) {
case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION:
break
case NodeTypes.ELEMENT:
case NodeTypes.ROOT:
traverseChildren(node, context)
break
}
context.currentNode = node
// 执行转换后要执行的操作
let i = exitFns.length
while (i--) {
exitFns[i]() // 可以假设转换已完成而执行的操作
}
}
export function traverseChildren(
parent: ParentNode,
context: TransformContext,
) {
for (let i = 0; i < parent.children.length; i++) {
const child = parent.children[i]
if (isString(child)) continue
context.parent = parent
context.childIndex = i
traverseNode(child, context)
}
}接下来,让我们谈谈具体的转换过程.作为示例,让我们实现 transformElement.
在 transformElement 中,我们主要将类型为 NodeTypes.ELEMENT 的节点转换为 VNodeCall.
export interface ElementNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.ELEMENT
tag: string
props: Array<AttributeNode | DirectiveNode>
children: TemplateChildNode[]
isSelfClosing: boolean
codegenNode: VNodeCall | SimpleExpressionNode | undefined
}
// ↓↓↓↓↓↓ 转换 ↓↓↓↓↓↓ //
export interface VNodeCall extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL
tag: string | symbol
props: PropsExpression | undefined
children:
| TemplateChildNode[] // multiple children
| TemplateTextChildNode
| undefined
}这是一个简单的对象到对象的转换,所以我认为不会很困难.让我们尝试通过阅读源代码来实现它. 我将粘贴我这次假设的代码以防万一.(指令支持将在另一章中完成.)
export const transformElement: NodeTransform = (node, context) => {
return function postTransformElement() {
node = context.currentNode!
if (node.type !== NodeTypes.ELEMENT) return
const { tag, props } = node
const vnodeTag = `"${tag}"`
let vnodeProps: VNodeCall['props']
let vnodeChildren: VNodeCall['children']
// props
if (props.length > 0) {
const propsBuildResult = buildProps(node)
vnodeProps = propsBuildResult.props
}
// children
if (node.children.length > 0) {
if (node.children.length === 1) {
const child = node.children[0]
const type = child.type
const hasDynamicTextChild = type === NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
if (hasDynamicTextChild || type === NodeTypes.TEXT) {
vnodeChildren = child as TemplateTextChildNode
} else {
vnodeChildren = node.children
}
} else {
vnodeChildren = node.children
}
}
node.codegenNode = createVNodeCall(vnodeTag, vnodeProps, vnodeChildren)
}
}
export function buildProps(node: ElementNode): {
props: PropsExpression | undefined
directives: DirectiveNode[]
} {
const { props } = node
let properties: ObjectExpression['properties'] = []
const runtimeDirectives: DirectiveNode[] = []
for (let i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
const prop = props[i]
if (prop.type === NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE) {
const { name, value } = prop
properties.push(
createObjectProperty(
createSimpleExpression(name, true),
createSimpleExpression(value ? value.content : '', true),
),
)
} else {
// directives
// TODO:
}
}
let propsExpression: PropsExpression | undefined = undefined
if (properties.length) {
propsExpression = createObjectExpression(properties)
}
return {
props: propsExpression,
directives: runtimeDirectives,
}
}基于转换后的 AST 的代码生成
由于我们为 Codegen 转换了 AST,我们也需要支持 Codegen. 对于进入 Codegen 的 AST,假设 VNodeClass(以及它们拥有的节点)编写代码就足够了. 期望的最终字符串表示与以前相同.
现有的 Codegen 实现非常简单,所以让我们在这里使它更正式一些(因为它相当硬编码). 让我们也创建一个 Codegen 特定的上下文并将生成的代码推送到其中. 此外,让我们在上下文中实现一些辅助函数(如缩进).
export interface CodegenContext {
source: string
code: string
indentLevel: number
line: 1
column: 1
offset: 0
push(code: string, node?: CodegenNode): void
indent(): void
deindent(withoutNewLine?: boolean): void
newline(): void
}我将在这里省略实现细节,但我只是为每个角色分离了函数,实现方法没有重大变化. 由于我还没有能够支持指令,由于在该区域删除了临时实现,有些部分不工作,但 如果代码大致按以下方式工作,就可以了!
import { createApp, defineComponent, ref } from 'chibivue'
const App = defineComponent({
setup() {
const count = ref(0)
return { count }
},
template: `
<div class="container">
<p> Hello World! </p>
<p> Count: {{ count }} </p>
</div>
`,
})
const app = createApp(App)
app.mount('#app')到此为止的源代码: chibivue (GitHub)
