数据绑定
想要绑定到模板
目前,我们直接操作 DOM,因此无法利用响应式系统或虚拟 DOM.
实际上,我们希望在模板部分编写事件处理程序和文本内容.这就是声明式 UI 的乐趣所在.
我们的目标是实现如下的开发者接口.
import { createApp, reactive, h } from 'chibivue'
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'Hello, chibivue!' })
const changeMessage = () => {
state.message += '!'
}
return { state, changeMessage }
},
render() {
return h('div', { class: 'container', style: 'text-align: center' }, [
h('h2', {}, `message: ${this.state.message}`),
h('img', {
width: '150px',
src: 'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/95/Vue.js_Logo_2.svg/1200px-Vue.js_Logo_2.svg.png',
}),
h('p', {}, [h('b', {}, 'chibivue'), ' is the minimal Vue.js']),
h('button', { onclick: this.changeMessage }, 'click me!'),
h(
'style',
{},
`
.container {
height: 100vh;
padding: 16px;
background-color: #becdbe;
color: #2c3e50;
}
`,
),
])
},
})
app.mount('#app')现在,我想能够在模板中处理从 setup 函数返回的值.
从现在开始,我将把这称为"模板绑定"或简称"绑定".
我将实现绑定,但在实现事件处理程序和 mustache 语法之前,有几件事我想做.
我提到了从 setup 返回的值,但目前 setup 的返回值要么是 undefined,要么是一个函数(渲染函数).
作为实现绑定的准备,我需要修改它,使 setup 可以返回状态和其他值,并且这些值可以作为组件数据存储.
export type ComponentOptions = {
setup?: (
props: Record<string, any>,
ctx: { emit: (event: string, ...args: any[]) => void },
) => Function | Record<string, unknown> | void
// 允许返回 Record<string, unknown>
// .
// .
// .
}export interface ComponentInternalInstance {
// .
// .
// .
setupState: Data // 将 setup 的结果作为对象存储在这里
}export const setupComponent = (instance: ComponentInternalInstance) => {
const { props } = instance.vnode
initProps(instance, props)
const component = instance.type as Component
if (component.setup) {
const setupResult = component.setup(instance.props, {
emit: instance.emit,
}) as InternalRenderFunction
// 根据 setupResult 的类型进行分支
if (typeof setupResult === 'function') {
instance.render = setupResult
} else if (typeof setupResult === 'object' && setupResult !== null) {
instance.setupState = setupResult
} else {
// do nothing
}
}
// .
// .
// .
}从现在开始,我将把在 setup 中定义的数据称为 setupState.
现在,在实现编译器之前,让我们思考如何将 setupState 绑定到模板.
之前,我们这样绑定 setupState:
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'hello' })
return () => h('div', {}, [state.message])
},
})嗯,这实际上不是真正的绑定,而是渲染函数简单地形成闭包并引用变量.
然而,这次,由于 setup 选项和渲染函数在概念上是不同的,我们需要找到一种方法将 setup 数据传递给渲染函数.
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'hello' })
return { state }
},
// 这将被转换为渲染函数
template: '<div>{{ state.message }}</div>',
})template 使用 h 函数编译为渲染函数并分配给 instance.render.
因此,它等价于以下代码:
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'hello' })
return { state }
},
render() {
return h('div', {}, [state.message])
},
})自然地,变量 state 在渲染函数内部没有定义.
现在,我们如何引用 state 变量?
使用 with 语句
总之,我们可以使用 with 语句来实现所需的结果:
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'hello' })
return { state }
},
render(ctx) {
with (ctx) {
return h('div', {}, [state.message])
}
},
})我相信有很多人不熟悉 with 语句.
这是有充分理由的,这个功能已被弃用.
根据 MDN:
虽然仍然被一些浏览器支持,但它已从 Web 标准中弃用。但是,它可能仍在用于各种目的,例如与遗留代码的兼容性。避免使用它,如果可能的话更新现有代码。
因此,建议避免使用它.
我们不知道 Vue.js 的实现将来会如何变化,但由于 Vue.js 3 使用 with 语句,我们将在此实现中使用它.
稍微说一下,Vue.js 中并非所有内容都使用 with 语句实现.
在处理单文件组件(SFC)中的模板时,它是在不使用 with 语句的情况下实现的.
我们将在后面的章节中介绍这一点,但现在,让我们考虑使用 with 来实现它.
现在,让我们回顾一下 with 语句的行为. with 语句扩展语句的作用域链.
它的行为如下:
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 }
with (obj) {
console.log(a, b) // 1, 2
}通过将包含 state 的父对象作为参数传递给 with,我们可以引用 state 变量.
在这种情况下,我们将把 setupState 视为父对象.
实际上,不仅是 setupState,来自 props 的数据和在 Options API 中定义的数据也应该是可访问的.
但是,现在,我们只考虑使用来自 setupState 的数据. (我们将在后面的部分中介绍这部分的实现,因为它不是最小实现的一部分.)
总结我们这次想要实现的内容,我们想要编译以下模板:
<div>
<p>{{ state.message }}</p>
<button @click="changeMessage">click me</button>
</div>转换为以下函数:
_ctx => {
with (_ctx) {
return h('div', {}, [
h('p', {}, [state.message]),
h('button', { onClick: changeMessage }, ['click me']),
])
}
}并将 setupState 传递给这个函数:
const setupState = setup()
render(setupState)实现 Mustache 语法
首先,让我们实现 Mustache 语法.
像往常一样,我们将考虑 AST,实现解析器,然后实现代码生成器.
目前,作为 AST 一部分定义的唯一节点是 Element,Text 和 Attribute.
由于我们想要定义 Mustache 语法,直觉上有一个叫做 Mustache 的 AST 是有意义的.
为此,我们将使用 Interpolation 节点.
Interpolation 有"插值"或"插入"等含义.
因此,我们这次将处理的 AST 将如下所示:
export const enum NodeTypes {
ELEMENT,
TEXT,
INTERPOLATION, // 添加
}
export type TemplateChildNode = ElementNode | TextNode | InterpolationNode // 添加 InterpolationNode
export interface InterpolationNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
content: string // Mustache 内部编写的内容(在这种情况下,在 setup 中定义的单个变量名将放在这里)
}现在 AST 已经实现,让我们继续实现解析器.
当我们找到字符串 {{ 时,我们将把它解析为 Interpolation.
function parseChildren(
context: ParserContext,
ancestors: ElementNode[]
): TemplateChildNode[] {
const nodes: TemplateChildNode[] = [];
while (!isEnd(context, ancestors)) {
const s = context.source;
let node: TemplateChildNode | undefined = undefined;
if (startsWith(s, "{{")) { // 这里
node = parseInterpolation(context);
} else if (s[0] === "<") {
if (/[a-z]/i.test(s[1])) {
node = parseElement(context, ancestors);
}
}
// .
// .
//
}function parseInterpolation(
context: ParserContext,
): InterpolationNode | undefined {
const [open, close] = ['{{', '}}']
const closeIndex = context.source.indexOf(close, open.length)
if (closeIndex === -1) return undefined
const start = getCursor(context)
advanceBy(context, open.length)
const innerStart = getCursor(context)
const innerEnd = getCursor(context)
const rawContentLength = closeIndex - open.length
const rawContent = context.source.slice(0, rawContentLength)
const preTrimContent = parseTextData(context, rawContentLength)
const content = preTrimContent.trim()
const startOffset = preTrimContent.indexOf(content)
if (startOffset > 0) {
advancePositionWithMutation(innerStart, rawContent, startOffset)
}
const endOffset =
rawContentLength - (preTrimContent.length - content.length - startOffset)
advancePositionWithMutation(innerEnd, rawContent, endOffset)
advanceBy(context, close.length)
return {
type: NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION,
content,
loc: getSelection(context, start),
}
}有些情况下 {{ 出现在文本中,所以我们将对 parseText 进行一些修改.
function parseText(context: ParserContext): TextNode {
const endTokens = ['<', '{{'] // 如果 <span v-pre>`{{`</span> 出现,parseText 结束
let endIndex = context.source.length
for (let i = 0; i < endTokens.length; i++) {
const index = context.source.indexOf(endTokens[i], 1)
if (index !== -1 && endIndex > index) {
endIndex = index
}
}
const start = getCursor(context)
const content = parseTextData(context, endIndex)
return {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT,
content,
loc: getSelection(context, start),
}
}对于那些到目前为止已经实现了解析器的人来说,应该没有特别困难的部分.
它只是搜索 {{ 并读取直到 }} 出现,生成 AST.
如果没有找到 }},它返回 undefined 并在 parseText 的分支中将其解析为文本.
让我们输出到控制台或其他地方,以确保解析正常工作.
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'Hello, chibivue!' })
const changeMessage = () => {
state.message += '!'
}
return { state, changeMessage }
},
template: `
<div class="container" style="text-align: center">
<h2>{{ state.message }}</h2>
<img
width="150px"
src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/95/Vue.js_Logo_2.svg/1200px-Vue.js_Logo_2.svg.png"
alt="Vue.js Logo"
/>
<p><b>chibivue</b> is the minimal Vue.js</p>
<button> click me! </button>
<style>
.container {
height: 100vh;
padding: 16px;
background-color: #becdbe;
color: #2c3e50;
}
</style>
</div>
`,
})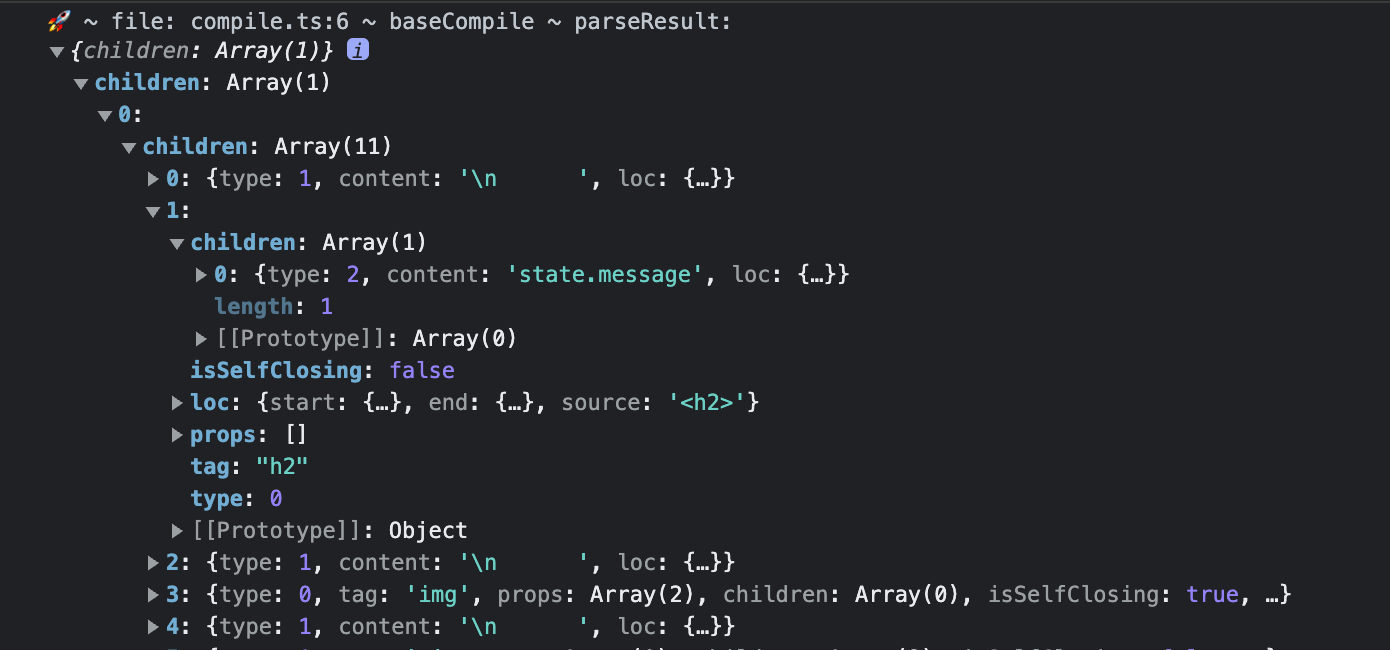
看起来不错!
现在让我们基于这个 AST 实现绑定.
用 with 语句包装渲染函数的内容.
export const generate = ({
children,
}: {
children: TemplateChildNode[]
}): string => {
return `return function render(_ctx) {
with (_ctx) {
const { h } = ChibiVue;
return ${genNode(children[0])};
}
}`
}
const genNode = (node: TemplateChildNode): string => {
switch (node.type) {
// .
// .
case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION:
return genInterpolation(node)
// .
// .
}
}
const genInterpolation = (node: InterpolationNode): string => {
return `${node.content}`
}最后,在执行渲染函数时,将 setupState 作为参数传递.\
~/packages/runtime-core/component.ts
export type InternalRenderFunction = {
(ctx: Data): VNodeChild // 接受 ctx 作为参数
}~/packages/runtime-core/renderer.ts
const setupRenderEffect = (
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
initialVNode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
) => {
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
const { render, setupState } = instance
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// .
// .
// .
const subTree = (instance.subTree = normalizeVNode(render(setupState))) // 传递 setupState
// .
// .
// .
} else {
// .
// .
// .
const nextTree = normalizeVNode(render(setupState)) // 传递 setupState
// .
// .
// .
}
}
}如果你已经走到这一步,你应该能够渲染了.让我们检查一下!

这完成了第一个绑定!
第一个指令
接下来是事件处理程序.
const genElement = (el: ElementNode): string => {
return `h("${el.tag}", {${el.props
.map(({ name, value }) =>
// 如果是 @click,将 props 名称转换为 onClick
name === '@click'
? `onClick: ${value?.content}`
: `${name}: "${value?.content}"`,
)
.join(', ')}}, [${el.children.map(it => genNode(it)).join(', ')}])`
}让我们检查操作.
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'Hello, chibivue!' })
const changeMessage = () => {
state.message += '!'
}
return { state, changeMessage }
},
template: `
<div class="container" style="text-align: center">
<h2>{{ state.message }}</h2>
<img
width="150px"
src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/95/Vue.js_Logo_2.svg/1200px-Vue.js_Logo_2.svg.png"
alt="Vue.js Logo"
/>
<p><b>chibivue</b> is the minimal Vue.js</p>
<button @click="changeMessage"> click me! </button>
<style>
.container {
height: 100vh;
padding: 16px;
background-color: #becdbe;
color: #2c3e50;
}
</style>
</div>
`,
})你做到了!做得好!完成了!
我想这样说,但实现还不够干净,所以我想稍微重构一下.
由于 @click 被归类为"指令"名称,很容易想象将来实现 v-bind 和 v-model.
所以让我们在 AST 中将其表示为 DIRECTIVE 并将其与简单的 ATTRIBUTE 区分开来.
像往常一样,让我们按照 AST -> parse -> codegen 的顺序实现它.
export const enum NodeTypes {
ELEMENT,
TEXT,
INTERPOLATION,
ATTRIBUTE,
DIRECTIVE, // 添加
}
export interface ElementNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.ELEMENT
tag: string
props: Array<AttributeNode | DirectiveNode> // props 是 AttributeNode 和 DirectiveNode 联合的数组
// .
// .
}
export interface DirectiveNode extends Node {
type: NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE
// 表示 `v-name:arg="exp"` 的格式。
// 例如,对于 `v-on:click="increment"`,它将是 { name: "on", arg: "click", exp="increment" }
name: string
arg: string
exp: string
}function parseAttribute(
context: ParserContext,
nameSet: Set<string>
): AttributeNode | DirectiveNode {
// 名称。
const start = getCursor(context);
const match = /^[^\t\r\n\f />][^\t\r\n\f />=]*/.exec(context.source)!;
const name = match[0];
nameSet.add(name);
advanceBy(context, name.length);
// 值
let value: AttributeValue = undefined;
if (/^[\t\r\n\f ]*=/.test(context.source)) {
advanceSpaces(context);
advanceBy(context, 1);
advanceSpaces(context);
value = parseAttributeValue(context);
}
// --------------------------------------------------- 从这里
// 指令
const loc = getSelection(context, start);
if (/^(v-[A-Za-z0-9-]|@)/.test(name)) {
const match =
/(?:^v-([a-z0-9-]+))?(?:(?::|^\.|^@|^#)(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+))?(.+)?$/i.exec(
name
)!;
let dirName = match[1] || (startsWith(name, "@") ? "on" : "");
let arg = "";
if (match[2]) arg = match[2];
return {
type: NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE,
name: dirName,
exp: value?.content ?? "",
loc,
arg,
};
}
// --------------------------------------------------- 到这里
// .
// .
// .const genElement = (el: ElementNode): string => {
return `h("${el.tag}", {${el.props
.map(prop => genProp(prop))
.join(', ')}}, [${el.children.map(it => genNode(it)).join(', ')}])`
}
const genProp = (prop: AttributeNode | DirectiveNode): string => {
switch (prop.type) {
case NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE:
return `${prop.name}: "${prop.value?.content}"`
case NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE: {
switch (prop.name) {
case 'on':
return `${toHandlerKey(prop.arg)}: ${prop.exp}`
default:
// TODO: 其他指令
throw new Error(`unexpected directive name. got "${prop.name}"`)
}
}
default:
throw new Error(`unexpected prop type.`)
}
}现在,让我们在游乐场中检查操作.
你应该能够处理不仅 @click,还有 v-on:click 和其他事件.
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const state = reactive({ message: 'Hello, chibivue!', input: '' })
const changeMessage = () => {
state.message += '!'
}
const handleInput = (e: InputEvent) => {
state.input = (e.target as HTMLInputElement)?.value ?? ''
}
return { state, changeMessage, handleInput }
},
template: `
<div class="container" style="text-align: center">
<h2>{{ state.message }}</h2>
<img
width="150px"
src="https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/95/Vue.js_Logo_2.svg/1200px-Vue.js_Logo_2.svg.png"
alt="Vue.js Logo"
/>
<p><b>chibivue</b> is the minimal Vue.js</p>
<button @click="changeMessage"> click me! </button>
<br />
<label>
Input Data
<input @input="handleInput" />
</label>
<p>input value: {{ state.input }}</p>
<style>
.container {
height: 100vh;
padding: 16px;
background-color: #becdbe;
color: #2c3e50;
}
</style>
</div>
`,
})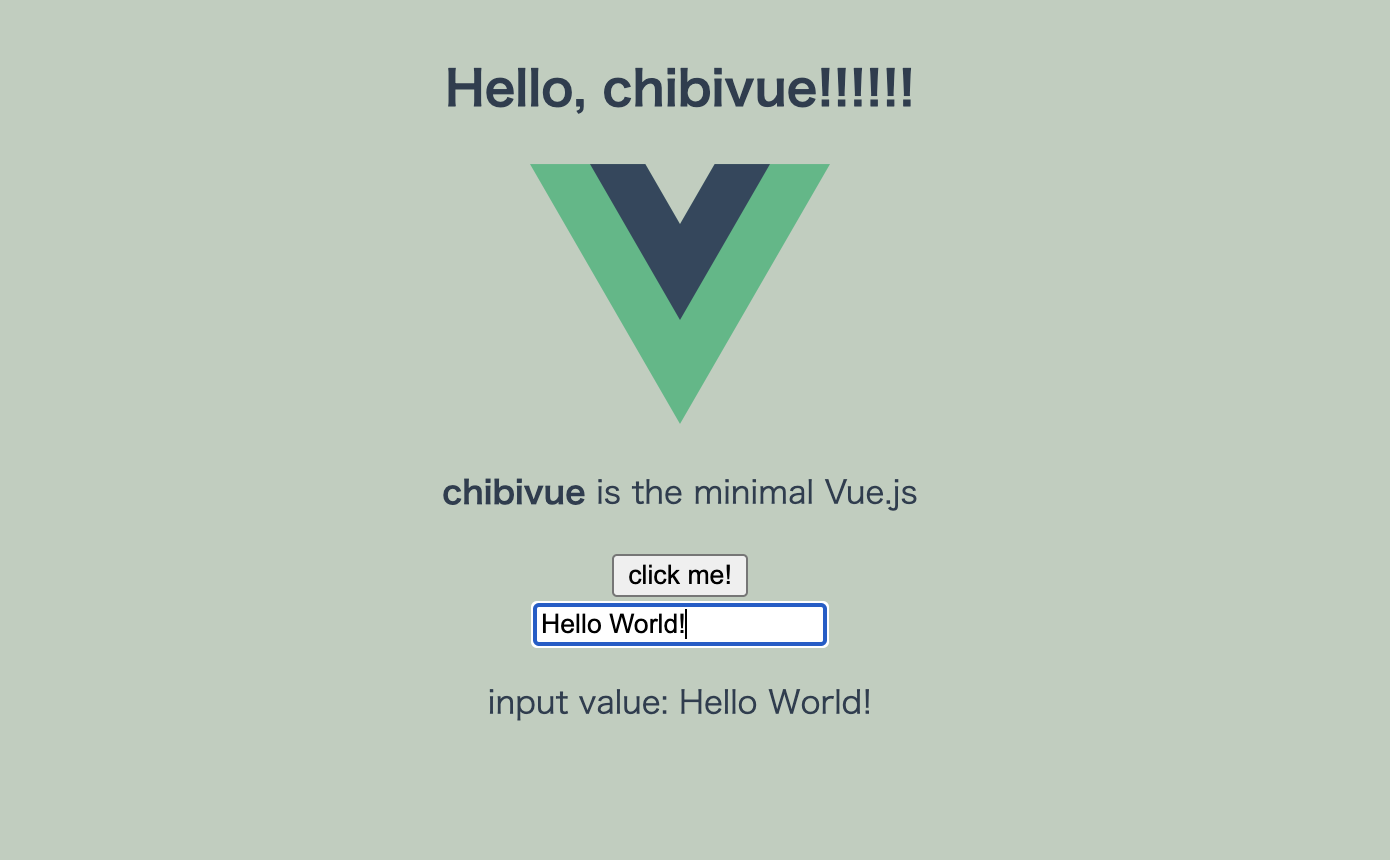
你做到了.
我们越来越接近 Vue 了!
有了这个,小模板的实现就完成了.做得好.
到此为止的源代码: chibivue (GitHub)
